In a Catalyzed Reaction a Reactant Is Often Called a
A substrate binds to. See answer 1 In an enzyme catalysed reaction a reactant is often called a substrate.
The Induced Fit Model.
. Adding energy to a reaction b decreasing the. For a reaction to reach the activation energy there must be some source that can input energy into the system. In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a.
Part A Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences Reset Help because it speeds up a chemical reaction without 1. A substrate is a reactant that is used by an enzyme. In general enzymes are what kinds of molecules.
Acid catalysts speed up the reaction by protonating. The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions increases with temperature up to a certain limit. Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gas or liquid phase.
In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a _____. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is reversible and occurs by SN1 pathway. Coenzymes are often broadly called cofactors but they are chemically.
An enzyme is considered ain. A carbohydrates b lipids. This process is called.
Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst. Free energy What are the two types of energy. Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a catalyst to it.
47 M solution of carbonic acid. In the general sense. Carbonic acid H₂CO₃ is a diprotic acid with Ka1 4.
After the reaction has proceeded the products are released and the enzyme can catalyze further reactions. Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after. A catalyst is a chemical substance that affects the rate of a chemical reaction by altering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed.
Substrate The energy available to do work. Add answer 5 pts. Thus a catalyst in this case sulfuric acid can be used to speed up a reversible reaction such as ester formation or its reverse ester hydrolysis.
When properly aligned the enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate ES ____ 6. The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called a substrate. Above a certain temperature enzyme activity decreases with temperature because of enzyme.
Because enzymes can increase reaction rates by enormous factors up to 10 17 times the uncatalyzed. In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a. What is the pH of a 0.
Often the energy source for reactions is heat. The catalyst is both a reactant and product in the reaction so it is not consumed. Substrate is a broadly used term but it is mainly used when talking about biochemical functions.
3 10⁷ and Ka2 5. One model of enzyme mechanism is called the induced fit. 21041 Mechanism of Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Esters.
A coenzyme is an organic non-protein compound that binds with an enzyme to catalyze a reaction. In a catalyzed reaction a reactant is often called a _____. A ____such as a vitamin binds to an enzyme and plays a role in catalysis.
Heterogeneous catalysis has at least four. Answer 1 of 3. The substance or substances initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents.
Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change and they yield. IUPAC gold book defines catalyst as A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without modifying the overall standard Gibbs energy change in the reaction.

Warm Update 10 1 Define These Words Chemical Reaction Reactant Product Activation Energy Catalyst Enzymes Substrate Ppt Download
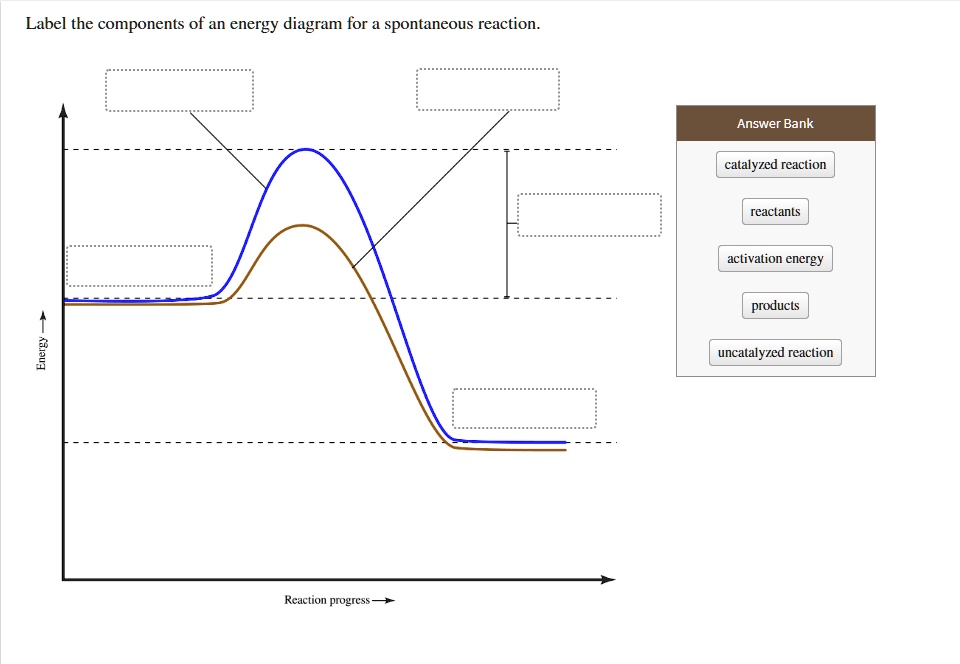
Solved Label The Components Of An Energy Diagram For A Spontaneous Reaction Answer Bank Catalyzed Reaction Reactants Aclivation Energy Products Uncatalyzed Reaction Reaction Progress 0
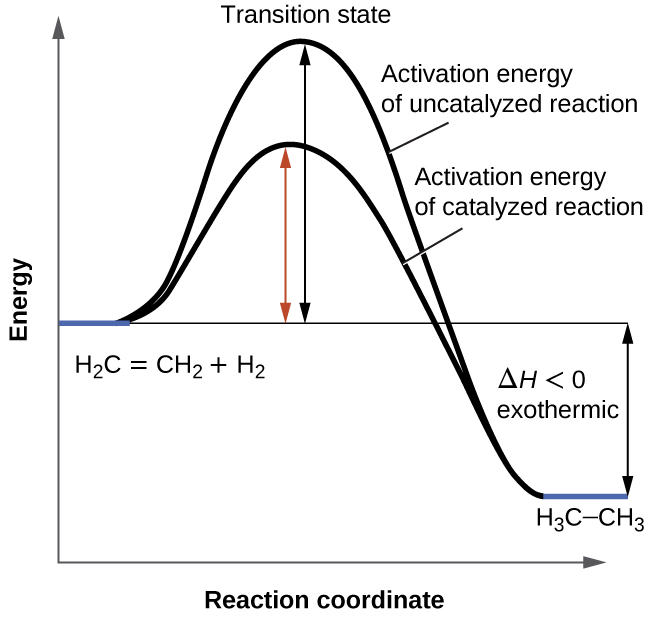
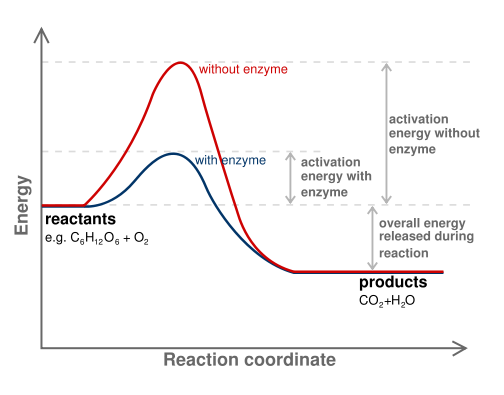
No comments for "In a Catalyzed Reaction a Reactant Is Often Called a"
Post a Comment